AUCTORES
Globalize your Research
Research Article | DOI: https://doi.org/DOI:10.31579/2688-7517/066
1 Department of Biotechnology, Microbiology and Human Nutrition, Faculty of Food Science and Biotechnology, University of Life Sciences in Lublin, Skromna 8, 20-704 Lublin, Poland.
2The Provincial Specialist Hospital in Biala Podlaska, Terebelska 57-65, 21-500 Biala Podlaska.
*Corresponding Author: Kinga Zdybel, Department of Biotechnology, Microbiology and Human Nutrition, Faculty of Food Science and Biotechnology, University of Life Sciences in Lublin, Skromna 8, 20-704 Lublin, Poland.
Citation: Kinga Zdybel, Angelika Śliwka, Magdalena P. Berecka, Paweł Polak and Adam Waśko., (2025), Postbiotics Formulation and Therapeutic Effect in Inflammation: A Systematic Review, J. Addiction Research and Adolescent Behaviour, 8(2) DOI:10.31579/2688-7517/066
Copyright: © 2025, Kinga Zdybel. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of The Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Received: 03 October 2025 | Accepted: 17 October 2025 | Published: 28 October 2025
Keywords: postbiotics; probiotics; non-live bacteria; inflammatory diseases; dysbiosis; gut microbiome; anti-inflammatory effects
Background: Postbiotics are bioactive compounds derived from inactivated probiotic microorganisms that show potential for preventing and treating inflammatory diseases. This review aimed to evaluate the evidence on their therapeutic effects in inflammatory conditions. Methods: A search of PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases from 2014 to 2024 identified 39 eligible studies. Article selection was conducted using the Rayyan platform, risk of bias was assessed with the Cochrane ROB 2 tool, and results were visualized with ROBVIS. Bibliometric networks were constructed using VOSviewer. Due to data heterogeneity, a meta-analysis was not performed; therefore, results were described and presented graphically. Results: The most commonly used microorganisms belonged to the Lactobacillaceae and Bifidobacteriaceae families, with heat inactivation as the predominant method. Postbiotics exert multifaceted anti-inflammatory effects by modulating cytokine expression, influencing immune cell signaling pathways, and strengthening epithelial barrier integrity. They regulate immune mechanisms such as the Th1/Th2 and Treg/Th17 balance, indicating their potential in treating inflammatory bowel diseases, autoimmune diseases, and metabolic syndrome. However, the heterogeneity of studies, their limitations, and risk of bias require cautious interpretation. Conclusions: Future research should focus on standardizing postbiotic preparations, conducting long- term clinical trials, and analyzing synergistic effects of different strains. Postbiotics offer a promising approach to managing inflammation, with potential applications in functional foods and nutraceuticals.
Postbiotics are a novel category of bioactive compounds derived from probiotic microorganisms that offer potential health benefits without the need for live microbes to be present. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) defines postbiotics as “preparations of inanimate microorganisms and/or their components that confer a health benefit on the host” [1]. This definition distinguishes postbiotics from probiotics and prebiotics, emphasising their microbial origin and non-viable nature. Postbiotics encompass various components, including microbial metabolites, cell wall fragments, short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), extracellular polysaccharides, peptides, and other cellular components [2,3] These compounds can modulate immune responses, enhance gut barrier function, and alter microbial ecology [4–6].The growing scientific interest in postbiotics has led to numerous preclinical and clinical studies investigating their potential therapeutic effects in various health contexts. Emerging evidence suggests that postbiotics may have beneficial effects on gastrointestinal diseases, metabolic diseases, atopic conditions, and even neuropsychiatric conditions by modulating the gut–brain axis [7–10]. One of the main mechanisms of action of postbiotics is their significant anti-inflammatory activity, which is attributed to the various components and bioactive fractions present in postbiotics [11]. A growing number of laboratory and clinical studies have suggested that chronic inflammation can lead to permanent damage to healthy organs, tissues, and cells, thereby increasing the risk of many common and fatal diseases. Because it plays a key role in the development and progression of various diseases, the development of effective prevention methods may provide promising support for anti-inflammatory therapies [12]. However, the current body of literature remains fragmented, with diverse formulations, target conditions, and outcome measures. This diversity limits the ability to draw clear conclusions regarding their efficacy and clinical relevance. Despite the growing research in this field, there is a lack of comprehensive systematic reviews synthesising the current evidence on postbiotic formulations and their therapeutic outcomes in chronic inflammatory conditions. Both in vitro and in vivo studies indicate that postbiotics are a promising approach for the prevention of inflammatory diseases by exerting a range of bioactivities, including antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities, modulation of the gastrointestinal microbiota, and enhancement of epithelial barrier function. However, the basic signalling pathways involved in their action remain incompletely understood and require further research [13]. This gap highlights the need for a structured overview of the field, identification of knowledge gaps, and guidance for future research and clinical applications of postbiotics to prevent and support the treatment of inflammatory conditions [14,15].The potential advantages of postbiotics over traditional probiotics include enhanced stability, standardisation, and safety. Unlike live probiotics, postbiotics are generally less affected by factors such as temperature, pH, or storage conditions. However, these factors can still influence the stability of certain biomolecules, such as LPS, depending on the specific range. Higher stability of postbiotics allows for easier incorporation into various food products and supplements, potentially expanding their applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Additionally, the use of non-viable microbial components may reduce the risk of adverse effects associated with the administration of live microorganisms, particularly in immunocompromised individuals or those with a compromised gut barrier function [16].Research on the mechanisms of action of postbiotics has revealed multiple pathways through which these compounds exert beneficial effects. For instance, certain postbiotic components have been shown to interact with pattern recognition receptors on immune cells, modulate inflammatory responses, and enhance innate immunity. Short-chain fatty acids, a common class of postbiotics, have been demonstrated to influence gene expression, metabolism, and cell function through various mechanisms, including histone deacetylase inhibition and G-protein–coupled receptor activation. Furthermore, some postbiotics have been found to exhibit antimicrobial properties, potentially contributing to the maintenance of a balanced gut microbiota and protection against pathogenic microorganisms [17].The diversity of postbiotic formulations and their potential applications presents both opportunities and challenges for researchers and clinicians. Although the range of bioactive compounds allows for targeted interventions in various health conditions, it also necessitates careful characterisation and standardisation of postbiotic preparations. Future research should focus on elucidating the specific bioactive components responsible for the observed health benefits, optimising dosing regimens, and investigating the potential synergistic effects of different postbiotic compounds. In the context of inflammation, research on the effects of postbiotics on the modulation of the inflammatory response is of particular importance. Elucidating the specific mechanisms of their action on the immune response at the cellular and molecular levels may contribute to the development of more effective and safer treatments for inflammatory diseases [18]. Therefore, this systematic review was conducted to evaluate and synthesise the current evidence on postbiotic formulations and their therapeutic effects in human and animal models of inflammation. The objective was to identify common patterns in formulation strategies, classify reported clinical or physiological outcomes, and critically assess the evidence quality. Through this approach, we seek to provide a structured overview of the field, highlight existing knowledge gaps, and inform future research directions and clinical applications of postbiotics in the context of supporting anti- inflammatory therapies in the body.
2.1.Protocol
The systematic review protocol was established based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA) statement [19]. To identify key research areas on probiotics, postbiotics, and gut microbiota, keyword co- occurrence analysis was conducted using VOSviewer (version 1.6.20) tool [20].
2.2.Eligibility Criteria:
To be eligible for inclusion, the studies had to include information on the use of postbiotics (formulation and supplementation) in human and animal models. These studies also had to contain information on the use of inactivated microorganisms for the treatment of different inflammation-related diseases in the body and their mechanisms of action. Studies on live microorganisms, in vitro research, reviews, and those published only as abstracts were excluded.
2.3.Sources Of Information and Search Strategy:
Systematic literature searches were performed using the following electronic bibliography databases: PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science, from 2014 to December 2024, without language restrictions on English. The literature search was based on keywords defined by the authors of this study. The selected search algorithm was as follows: ((((((Postbiotics)) OR (Postbiotic formulations)) OR (Postbiotic supplementation)) AND (((bacteria treatment) OR (microorganisms)) OR (formulation))) AND ((dysfunction) OR (diseases))) AND (((((therapeutic effects) OR (clinical trials)) OR (health)) OR (treatment)) OR (therapy)) NOT (review). The search algorithm was tailored according to the structure of each database. One researcher downloaded the Research Information Systems (RIS) file generated by each database and uploaded it to the VOSviewer software tool, which enabled the construction and visualisation of bibliometric networks. The Research Information Systems (RIS) file generated by each database was also uploaded to the Rayyan® web application for systematic reviews [21].
2.4.Selection Process:
The selection of articles for inclusion in the review was conducted in two stages using Rayyan®, which allows reviewers to blind the selection process. In the first stage, titles and abstracts were analysed based on the inclusion criteria. In the second stage, full-text arti- cles were assessed to confirm their eligibility. At both stages, each article was inde- pendently reviewed by three researchers. In cases of disagreement, the study was reas- sessed and resolved through discussion.
2.5.Data Extraction:
Three authors independently extracted data from each included study using the Ray- yan® platform. The extracted data included the first author, year of publication, and meth- odological details, such as the type of study conducted, population (species, age, sex, and sample size), type of disease studied, intervention (species or strain of microorganisms, method of inactivation, postbiotic formulation, dosage, and duration of administration), and outcomes (method of application and mechanisms of action of postbiotics in different diseases).
2.6.Risk Of Bias in Individual Studies:
The risk assessment for each study was conducted independently by three authors using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool (ROB 2) [22]. The ROBVIS tool was also used to visualise risk assessments [23]. As required by ROB 2, the following parameters were in- dependently assessed: (1) risk due to the randomisation process; (2) risk due to deviations from the intended interventions; (3) risk due to missing outcome data; (4) risk due to the measurement of the outcome; and (5) risk due to the selection of the reported result. Tool ROB 2 was used to analyse the overall risk of bias, represented as high risk in red, risk uncertainty in yellow, and low risk in green. Any differences in bias assessment were re- solved through discussions among the three authors until an agreement was reached.
2.7.Data Synthesis:
Meta-analysis was not possible due to the heterogeneity of the included studies, which was due to several factors. First, the review included both human and animal stud- ies. Second, the studies included both single-strain and multi-strain postbiotic prepara- tions. Third, the formulation of postbiotics and the forms of administration were diverse. Furthermore, the methods used to assess the therapeutic potential of postbiotics varied between studies. The duration of the intervention also varied greatly, from a few days to a year. Therefore, the results were presented in the form of structured graphs divided into groups (type of study, disease, single-strain postbiotic preparations, multi-strain postbi- otic preparations, inactivation method, formulation, and method of administration). All data within groups were summed and presented as percentages.
3.1.Summary of Studies:
To ascertain the predominant research domains in the literature concerning probiot- ics, postbiotics, and gut microbiota, a co-occurrence analysis of keywords was performed using VOSviewer software. This analysis encompassed the terms present in the titles and abstracts of the publications selected for review. The findings are shown in Figure 1. The resulting map revealed four distinct thematic clusters, illustrating the interdisciplinary nature of the study area. The red cluster is centred on clinical research involving humans. Dominant terms, such as humans, gastrointestinal microbiome, microbiota, probiotics, fe- males, and males, indicate a broad interest in the impact of gut microbes on human health, including sex differences and intervention designs (e.g., the double-blind method). The blue cluster encompasses inflammatory and immune-related topics of research. The pres- ence of terms such as inflammatory bowel disease, colitis, oxidative stress, and inflamma- tion confirms the significance of preclinical research in analysing the mechanisms of action of probiotics and postbiotics in the context of gastrointestinal pathology. The green cluster represents the domain of animal experiments. The frequent co-occurrence of terms such as animals, mice, gut microbiota, postbiotics, and dietary supplements indicates the use of animal models to assess the function and efficacy of microbiological interventions. The yellow cluster focused on the biotechnological aspects of formulations and active ingredi- ents. Terms such as Lactobacillus plantarum, cytokines, lipopolysaccharides, and obesity reflect the interest in specific bacterial strains, their metabolites, and their effects on meta- bolic and immunological parameters of obesity. Many studies on probiotics, postbiotics, inflammation, and the gastrointestinal microbiome have confirmed the centrality of these issues in the current scientific discourse. The density of connections and overlapping clus- ters suggests an intense integration of clinical, experimental, and technological perspectives.
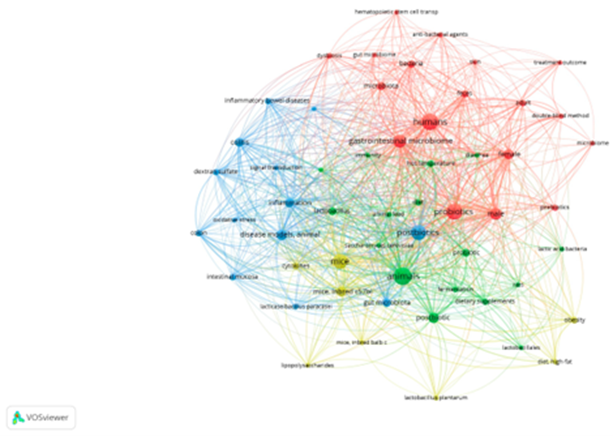
Figure 1: Co-occurrence networks of all 38 keywords that appeared at least 7 times. The keyword networks are coloured according to the four clusters generated, which indicate inter-relationships. Publication selection for this systematic
Review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines. A total of 283 bibliographic records were identified in 3 databases: PubMed (n = 153), Scopus (n = 80), and Web of Science (n = 50). After the removal of 74 duplicate records, 209 unique items were screened. An analysis of the titles and abstracts led to the exclusion of 145 publications, resulting in 64 full-text articles being evaluated for eligibility. Of these, 25 studies were excluded from further analysis for the following reasons: lack of information on the inactivation method used (n = 13), lack of information on the microorganisms used (n = 5), unavailable full text of publication (n = 5), other med- ical diseases (n = 1), and studies that were in vitro experiments (n = 1). Ultimately, 39 stud- ies met the eligibility criteria and were included in the review. The details of the selection process are shown in the PRISMA diagram (Figure 2).
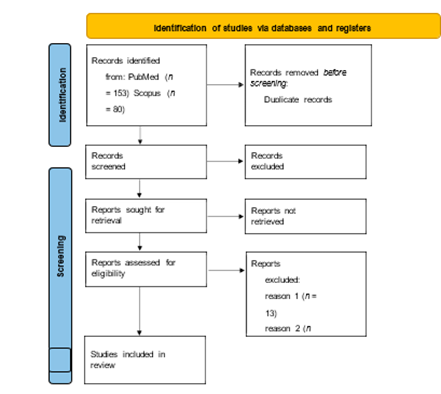
Figure 2. PRISMA flow diagram summarising the article selection process and reasons for exclusion: reason 1—lack of information on inactivation method (n = 13); reason 2—lack of information on the microorganisms used (n = 5); reason 3—not available full text of publication; reason 4—other medical diseases (n = 1); reason 5—studies that are in vitro experiments (n = 1). PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis.The following summary presents the data extracted from Table 1, which delineates the characteristics of the studies included in this systematic review, with a particular focus on the type of microbiota-based interventions, administration routes, microbial strains used, and clinical contexts
Figure 2. PRISMA flow diagram summarising the article selection process and reasons for exclusion: reason 1—lack of information on inactivation method (n = 13); reason 2—lack of information on the microorganisms used (n = 5); reason 3—not available full text of publication; reason 4—other medical diseases (n = 1); reason 5—studies that are in vitro experiments (n = 1). PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis. The following summary presents the data extracted from Table 1, which delineates the characteristics of the studies included in this systematic review, with a particular focus on the type of microbiota-based interventions, administration routes, microbial strains used, and clinical contexts. Among the 39 studies analysed, experimental design was predominant (74.4%), with a significant proportion of randomised trials (23.1%), indicating a relatively high method- ological standard in the field of microbiota-targeted interventions (Figure 3A). The inter- ventions addressed a broad spectrum of clinical conditions associated with inflammatory responses (N = 41), most frequently gastrointestinal diseases (46.3%), followed by meta- bolic and endocrine diseases (14.6%), liver and kidney diseases (9.8%), and infectious, der- matological, oral, neurological, and musculoskeletal conditions (Figure 3B). In the subset of single-strain interventions (N = 68), the most frequently used genera included Lactica- seibacillus, Lactiplantibacillus, and Limosilactobacillus, belonging to the family Lactobacillaceae (67.6%). The second and third most frequently used bacteria were from the Bifidobacteri- aceae (19.6%) and Akkermansiaceae (4.4%) families, respectively. The most common indi- vidual strains were L. plantarum, L. casei, B. animalis, and S. thermophilus (Figure 3C). Multi- strain formulations typically contained three to eight strains, most frequently combining L. casei, L. plantarum, B. animalis, B. longum, and L. reuteri, reflecting a preference for well- characterized strains from the Lactobacillaceae and Bifidobacteriaceae families due to their established safety profiles and immunomodulatory potential (Figure 3D). Regarding in- activation methods, heat-killing was the most frequently employed technique (84.6%), in- cluding sterilisation, pasteurisation, and tyndallization, whereas other methods such as freeze-thawing, ultracentrifugation, spray-drying, enzyme treatment, and UV radiation were rarely used (2.6?ch) (Figure 3E). Suspensions were the most commonly used de- livery form (66.7%), followed by fluids and capsules (7.7?ch), with pills, gels, lozenges, and advanced carriers, such as pectin-zein beads, appearing in isolated cases (Figure 3F). Oral administration was the predominant route of administration (61.5%), with additional studies employing oral (23.1%) or intragastric gavage (5.1%). Alternative administration routes, such as intranasal, vaginal, ocular, or topical, were reported infrequently (2.6?ch), indicating the primary intestinal target of postbiotic interventions, while also high- lighting the emerging interest in systemic or localised extraintestinal effects (Figure 3G). Figure 4. illustrates the research methodologies employed by the authors in the pub- lications analysed from 2019 to 2024. The figure presents a heat map where each rectan- gle s colour corresponds to a specific analytical or molecular method, and the vertical axis lists the authors names organised by the year of publication. Among the techniques used, ELISA emerged as the most frequently employed method, appearing in 24 publications, underscoring its significance in quantifying cytokines and other immune biomarkers in studies on microbiota, probiotics, and postbiotics. Other prevalent methods included 16S rDNA sequencing, featured in 11 publications, which is extensively used to examine gut microbiota composition, and Western blotting, featured in 11 publications, primarily for detecting signalling proteins linked to inflammation or immune response. RT-qPCR and qPCR were used in four studies to assess gene expression and the presence of bacterial genetic material. The remaining methods appeared sporadically in only one or two pub- lications and encompassed highly specialised techniques, such as LC-MS/MS, UPLC-Q- TOF-MS, metagenomic sequencing, SMRT sequencing, microbiome assays, and spectro- photometry. This diversity of methods reflects a broad spectrum of research approaches, ranging from classical immunological analyses to advanced omics techniques, including metabolomics, metagenomics, and transcriptomics. A notable increase in unique tech- niques was observed in 2023–2024 publications, indicating escalating research complexity and advancing methodological specialisation. Integrated analytical approaches that com- bine molecular methods with metabolite profiling and next-generation sequencing are be- coming increasingly prevalent. The analysis of research methodologies revealed a pre- dominance of techniques related to immunology and microbiota analysis, such as ELISA and 16S rDNA, while also expanding the methodological spectrum toward advanced molecular and omics analyses. This trend suggests a growing need for multilevel analyses of the intricate interactions between probiotics, microbiota, and host responses.

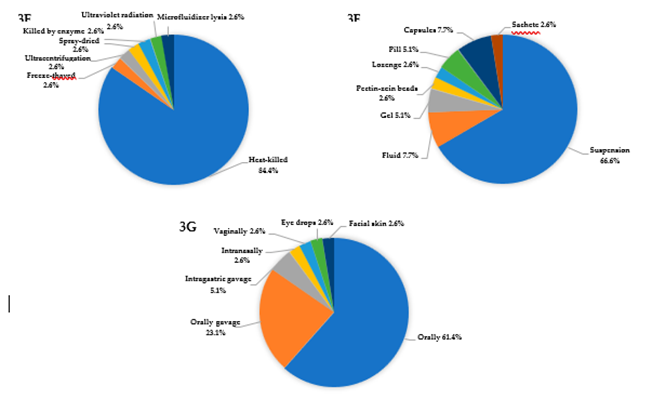
Figure 3. Characteristics of postbiotics used in research on inflammatory disease: (A) Study design,(B) type of disease, (C) single-strain postbiotics, (D) multiple-strain postbiotics, (E) method of inac- tivation, (F) forms of postbiotics formulation, (G) postbiotics applications method.
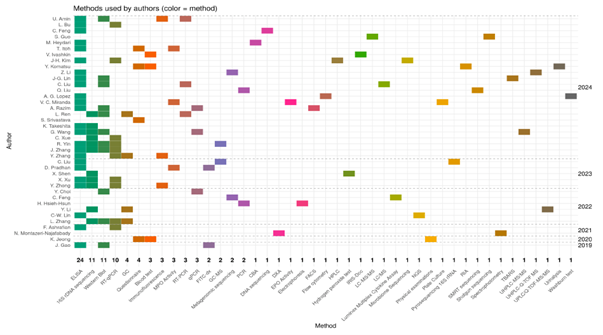
Figure 4: The heat map illustrates the research methodologies used by the authors in the publica- tions analysed between 2019 and 2024. The values on the X axis indicate the number of publications in which the method was used. [24–62]
3.2.Risk of Bias:
The risk of bias in the included studies, shown in Figure 5, indicates that the overall risk of bias was a concern. Not all studies described the generation of random sequences in detail, and 26 reported correct allocation concealment methods. Most studies had an overall risk of bias owing to deviations from the intended intervention. All studies had a low risk of bias regarding missing outcome data. In contrast, only 16 studies had a low risk of bias for outcome measures. For most studies, the risk of reporting bias was unclear.
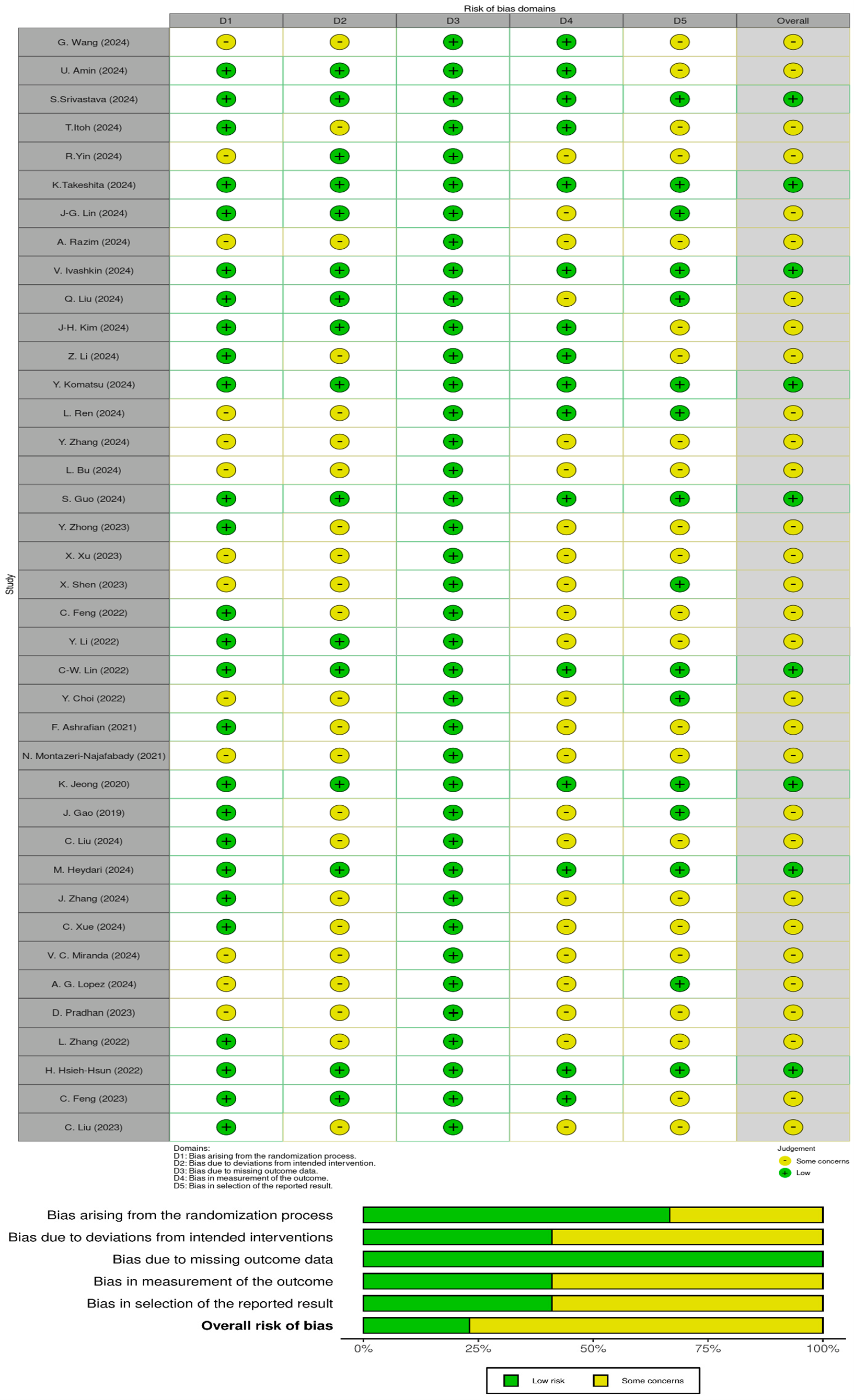
Figure 5. Risk of bias in the included studies. [24–62]
The findings of this systematic review offer a comprehensive examination of the cur- rent understanding of the formulation of postbiotics and their application in the treatment and prevention of inflammation. Postbiotics are considered safer than probiotics because they do not require the presence of live microorganisms to exert beneficial effects on health. Therefore, the risk of interaction between inactivated microorganisms and host microbiota is eliminated [63]. Studies have highlighted the increasing interest in the therapeutic potential of postbiotics as a safe and stable alternative to probiotics, especially in vulnerable populations, such as individuals with compromised intestinal barriers or immunosuppression [1,16]. Research indicates that postbiotics can effectively modulate the immune response, demonstrating anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and protective effects on intesti- nal epithelial integrity [11,13]. The composition of postbiotic preparations is contingent on the bacterial strain, method of inactivation, and processing technique employed. The most frequently utilised bacteria belong to the genera Lactobacillus (e.g., L. plantarum and L. casei) and Bifidobacterium (e.g., B. animalis), whereas Gram-negative bacteria, such as Akkermansia muciniphila, are employed less frequently [64,65]. Strain selection determines the composition of the bioactive components. Preparations derived from Gram-positive bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, are rich in metabolites such as SCFAs, peptides, and EPS, which contribute to their anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties. Conversely, postbiotics derived from Gram-negative bacteria, although used less frequently, contain bioactive membrane components (e.g., LPS) that exhibit immuno- regulatory activity [17]. The presence of a variety of active substances in the cellular composition of postbiot- ics makes the selection of an appropriate microbial inactivation method, tailored to the specific strain, a key aspect to maintain the integrity and biological activity of these com- ponents. The predominance of heat inactivation as the primary processing technique, uti- lised in 84.6% of the cases analysed, indicates its practicality and scalability in postbiotic production. However, alternative methods, including UV radiation, enzymatic lysis, and freeze-drying, warrant further exploration to determine their effects on the preservation of biological activity [66]. Research has elucidated that the mechanisms through which postbiotics exert their effects include the suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokine [removed]IL-6 and TNF- α), activation of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as TLR2 and TLR4, modifica- tion of signalling pathways including NF-κB, MAPK, and NLRP3, and enhancement of intestinal barrier function via the expression of tight junction proteins [4,67]. In certain contexts, postbiotics have been observed to influence the Treg/Th17 balance, which is of particular significance in the management of inflammatory bowel disease. This modula- tion of immune responses supports epithelial integrity and mitigates immune-mediated damage to the gut. Conversely, numerous studies have demonstrated that postbiotics ex- ert anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting signalling pathways [68]. Postbiotics, such as sodium butyrate, have shown promise in glycaemic control by improving islet morphol- ogy and downregulating the NF-κB–mediated inflammatory signalling pathway in strep- tozotocin-induced T1D mice. This indicates that postbiotics can attenuate inflammation by suppressing key pro-inflammatory signalling [69]. Postbiotics have been shown to sig- nificantly modulate the composition of gut microbiota. Postbiotic interventions have re- sulted in an enriched composition of beneficial gut bacteria, including B. animalis, L. sali- varius, and A. muciniphila. These bacteria contribute to gut barrier integrity and immune homeostasis, indirectly supporting intestinal epithelial protection [16,64]. Closely related to this effect of postbiotics is protection against gut dysbiosis and leaky gut. By restoring microbiota balance and inhibiting pathogenic bacterial growth, postbiotics help prevent dysbiosis-induced damage to the intestinal mucosa, reducing endotoxin (LPS) transloca- tion and systemic inflammation, which exacerbates T1D [69]. It has also been demon- strated that postbiotics containing microbial metabolites, such as SCFAs, can influence the balance of the Th1/Th2 immune response, which is crucial in the context of allergies and autoimmune diseases [63]. Other components of postbiotic preparations with proven ben- eficial effects include bacterial enzymes, tryptophan derivatives such as melatonin, fer- mentation products such as lactic acid and isocaproic acid, and secondary metabolites e.g., colipterins from E. coli and thioredoxins from S. boulardii), which have demonstrated immunomodulatory properties that contribute to beneficial effects against IBD, both in vitro and in vivo [70]. Similarly, beneficial effects have been observed for EPS secreted by probiotic strains, such as Lactobacillus helveticus and L. rhamnosus, which ameliorate gut inflammation by enhancing antioxidant defences and supporting barrier integrity [71,72]. Finally, several low-molecular-weight components of postbiotic formulations also exhibit antioxidant properties by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and enhancing the ac- tivity of antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). This activity mitigates oxidative stress, which exacerbates inflammation and epithelial damage [73]. Although most evidence supporting the thera- peutic efficacy of postbiotics is derived from gastrointestinal studies, beneficial effects have also been observed in metabolic, dermatological, and neurological diseases [5]. The overall risk of bias found in the included studies raises doubts about the reliabil- ity of the results presented. Although all studies showed a low risk of bias related to miss- ing outcome data, other domains showed significant methodological shortcomings. The process of random sequence generation was not consistently reported, and only 26 studies provided clear information on allocation concealment. The majority of studies showed some concern or high risk for deviations from the intended interventions, which may have affected the internal validity of the results. In addition, only 16 studies reported a low risk of bias in outcome measurement, and the risk of selective reporting remained unclear in many cases. These issues suggest that although some methodological aspects were ade- quately addressed, caution should be exercised when interpreting results.This systematic review has several limitations. First, the significant heterogeneity among the included studies—particularly regarding postbiotic formulations, inactivation methods, types of inflammatory conditions, and outcome measures—limits the generali- zability of the findings and precludes the possibility of conducting a meta-analysis. The diversity in study designs, intervention protocols, and analytical techniques (e.g., ELISA, 16S rRNA, qPCR, and omics approaches) poses challenges for directly comparing results, leading to variability and inconsistent conclusions. Additionally, methodological differ- ences, such as the lack of standardisation in sample preparation, sequencing methods, and extraction techniques (e.g., centrifugation, ultrafiltration, chromatography, and mass spectrometry), further impede comparability across studies. A significant limitation is that the included studies involved many different inflammatory pathologies with different or- igins and mechanisms of action. Inflammation, which is a response of the immune system to a variety of harmful agents, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or toxins, can take dif- ferent forms. This pathophysiological heterogeneity may cause variability in the response to postbiotics and introduce potential bias into the results of the review. The different mechanisms and severity of inflammation in individual conditions make it difficult to di- rectly compare therapeutic effects and to interpret the data at an overall level. Second, most of the included studies were preclinical or animal-based, which re- stricts the applicability of findings to human health outcomes. The limited number of clin- ical trials, along with small sample sizes and short intervention periods, weakens the strength of the evidence and limits the ability to draw robust, evidence-based recommen- dations. Third, many studies did not clearly report randomisation procedures or allocation concealment, increasing the risk of bias. Despite the use of rigorous selection criteria, these reporting deficiencies raise concerns about internal validity. Finally, publication bias may be present, as studies with positive outcomes are more likely to be published, potentially leading to an overestimation of the therapeutic potential of postbiotics. Therefore, well-designed, large-scale randomised controlled trials with long-term follow-up and standardised methodologies are urgently needed to validate the efficacy and safety of postbiotic interventions in chronic inflammatory conditions. Based on the data obtained, postbiotics should be regarded as promising adjunctive therapy components and potential functional food components. Their stability, safety, and capacity for precise formulation render them particularly valuable nutraceutical products. Future efforts should focus on developing standards for determining the content of active components, standardising inactivation methods, and conducting long-term, multicentre clinical trials. Additionally, it is recommended to analyse the synergistic effects of differ- ent strains and integrate clinical studies with metagenomic and metabolomic data to en- hance the understanding of the interactions between postbiotics, microbiota, and the host immune system. It is particularly important to consider the individual characteristics of the microbiome and the inflammatory state of the patient to facilitate the creation of per- sonalised postbiotic therapies. The implementation of such approaches may contribute not only to improving the health of patients with chronic inflammatory conditions but also to the development of effective preventive strategies for health and nutrition policies. In contemporary nutrition and dietetics, postbiotics are emerging as pivotal compo- nents of the next generation of functional ingredients. Their primary advantage over pro- biotics is the elimination of risks associated with live microorganisms, which is particu- larly significant for individuals with dysbiosis, autoimmune diseases, or compromised immune systems [1]. Postbiotics are increasingly being considered for integration into standard dietary interventions and as adjuncts in the pharmacotherapy of inflammatory and metabolic diseases. Owing to their chemical stability and resilience to varying storage conditions, postbiotics can be seamlessly incorporated into diverse food matrices, ranging from fermented dairy products to capsules and powder formulations. This characteristic also enhances their commercial appeal compared to probiotics, which necessitate the via- bility of microorganisms until consumption. From a biotechnological standpoint, postbi- otics present novel opportunities for optimising fermentation processes and designing bi- oactive ingredients through metabolic engineering. Notable examples include formula- tions aimed at producing specific metabolites, such as butyrate, propionate, and bioactive peptides, which possess anti-inflammatory, antitumour, and neuroprotective properties[13,17]. However, despite their great application potential, the implementation of postbiotics in clinical and dietary practices poses several normative and technological challenges. Currently, there is a lack of clear regulatory guidelines specifying the safety, efficacy, and labelling requirements for postbiotic products. Therefore, interdisciplinary cooperation among microbiologists, biotechnologists, nutritionists, and regulators is required to create standards to ensure the quality and efficacy of formulations available on the market. In the near future, it will be important to develop translational research that combines mo- lecular analyses with clinical observations to better understand the relationship between postbiotic ingredients, microbiota, and host response.
This systematic review provides compelling evidence supporting the potential of postbiotics as safe and effective agents for the prevention and treatment of inflammation- related diseases. The absence of live microorganisms in postbiotic formulations eliminates the risk of adverse host–microbiota interactions, making them particularly suitable for vulnerable populations, such as immunocompromised individuals. This review aimed to identify patterns in formulation strategies, classify reported outcomes, and assess the quality of evidence. The most frequently used microorganisms belong to the Lactobacil- laceae and Bifidobacteriaceae families. The results of this review indicate that the formulation of postbiotic preparations plays a critical role in determining their therapeutic potential for the management of chronic inflammation. Key factors influencing the efficacy of post- biotics include the selection of microbial strains, methods of inactivation, and processing conditions applied.Based on the reviewed studies, thermal inactivation emerged as the most commonly employed technique, likely because of its operational simplicity and scalability. Nonethe- less, given the susceptibility of cellular components to thermal degradation and the im- portance of preserving their biological activity, alternative inactivation methods (although less frequently utilized) should also be considered, as they were reported in several of the analysed publications.Therapeutically, postbiotics exert multifaceted anti-inflammatory effects by modu- lating cytokine expression, influencing immune cell signalling pathways, and reinforcing epithelial barrier integrity. Their ability to regulate key immune mechanisms, such as Th1/Th2 and Treg/Th17 balance, makes them promising candidates for adjunctive treat- ment of chronic inflammatory conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease, meta- bolic syndrome, and autoimmune diseases. These findings underscore the importance of strain-specific and process-tailored formulation strategies to maximise the therapeutic ef- ficacy of postbiotics in clinical settings.However, many studies have methodological limitations, and the overall risk of bias is concerning. Future research should focus on standardising postbiotic preparations, con- ducting long-term clinical trials, and analysing the synergistic effects of different strains.
Author Contributions: Conceptualization, K.Z., A.W., M.P.-B. and A.Ś.; literature search, K.Z. and A.W.; literature screening and selection, K.Z., A.W. and M.P.-B.; risk of bias analysis, K.Z. and A.Ś.; data analysis, K.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, K.Z. and A.W.; critical revision and editing, K.Z., A.W., M.P.-B. and P.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding: This research received no external funding.
Conflicts Of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Clearly Auctoresonline and particularly Psychology and Mental Health Care Journal is dedicated to improving health care services for individuals and populations. The editorial boards' ability to efficiently recognize and share the global importance of health literacy with a variety of stakeholders. Auctoresonline publishing platform can be used to facilitate of optimal client-based services and should be added to health care professionals' repertoire of evidence-based health care resources.

Journal of Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Intervention The submission and review process was adequate. However I think that the publication total value should have been enlightened in early fases. Thank you for all.

Journal of Women Health Care and Issues By the present mail, I want to say thank to you and tour colleagues for facilitating my published article. Specially thank you for the peer review process, support from the editorial office. I appreciate positively the quality of your journal.
Journal of Clinical Research and Reports I would be very delighted to submit my testimonial regarding the reviewer board and the editorial office. The reviewer board were accurate and helpful regarding any modifications for my manuscript. And the editorial office were very helpful and supportive in contacting and monitoring with any update and offering help. It was my pleasure to contribute with your promising Journal and I am looking forward for more collaboration.

We would like to thank the Journal of Thoracic Disease and Cardiothoracic Surgery because of the services they provided us for our articles. The peer-review process was done in a very excellent time manner, and the opinions of the reviewers helped us to improve our manuscript further. The editorial office had an outstanding correspondence with us and guided us in many ways. During a hard time of the pandemic that is affecting every one of us tremendously, the editorial office helped us make everything easier for publishing scientific work. Hope for a more scientific relationship with your Journal.

The peer-review process which consisted high quality queries on the paper. I did answer six reviewers’ questions and comments before the paper was accepted. The support from the editorial office is excellent.

Journal of Neuroscience and Neurological Surgery. I had the experience of publishing a research article recently. The whole process was simple from submission to publication. The reviewers made specific and valuable recommendations and corrections that improved the quality of my publication. I strongly recommend this Journal.

Dr. Katarzyna Byczkowska My testimonial covering: "The peer review process is quick and effective. The support from the editorial office is very professional and friendly. Quality of the Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions is scientific and publishes ground-breaking research on cardiology that is useful for other professionals in the field.
Thank you most sincerely, with regard to the support you have given in relation to the reviewing process and the processing of my article entitled "Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of The Prostate Gland: A Review and Update" for publication in your esteemed Journal, Journal of Cancer Research and Cellular Therapeutics". The editorial team has been very supportive.

Testimony of Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology: work with your Reviews has been a educational and constructive experience. The editorial office were very helpful and supportive. It was a pleasure to contribute to your Journal.

Dr. Bernard Terkimbi Utoo, I am happy to publish my scientific work in Journal of Women Health Care and Issues (JWHCI). The manuscript submission was seamless and peer review process was top notch. I was amazed that 4 reviewers worked on the manuscript which made it a highly technical, standard and excellent quality paper. I appreciate the format and consideration for the APC as well as the speed of publication. It is my pleasure to continue with this scientific relationship with the esteem JWHCI.

This is an acknowledgment for peer reviewers, editorial board of Journal of Clinical Research and Reports. They show a lot of consideration for us as publishers for our research article “Evaluation of the different factors associated with side effects of COVID-19 vaccination on medical students, Mutah university, Al-Karak, Jordan”, in a very professional and easy way. This journal is one of outstanding medical journal.
Dear Hao Jiang, to Journal of Nutrition and Food Processing We greatly appreciate the efficient, professional and rapid processing of our paper by your team. If there is anything else we should do, please do not hesitate to let us know. On behalf of my co-authors, we would like to express our great appreciation to editor and reviewers.

As an author who has recently published in the journal "Brain and Neurological Disorders". I am delighted to provide a testimonial on the peer review process, editorial office support, and the overall quality of the journal. The peer review process at Brain and Neurological Disorders is rigorous and meticulous, ensuring that only high-quality, evidence-based research is published. The reviewers are experts in their fields, and their comments and suggestions were constructive and helped improve the quality of my manuscript. The review process was timely and efficient, with clear communication from the editorial office at each stage. The support from the editorial office was exceptional throughout the entire process. The editorial staff was responsive, professional, and always willing to help. They provided valuable guidance on formatting, structure, and ethical considerations, making the submission process seamless. Moreover, they kept me informed about the status of my manuscript and provided timely updates, which made the process less stressful. The journal Brain and Neurological Disorders is of the highest quality, with a strong focus on publishing cutting-edge research in the field of neurology. The articles published in this journal are well-researched, rigorously peer-reviewed, and written by experts in the field. The journal maintains high standards, ensuring that readers are provided with the most up-to-date and reliable information on brain and neurological disorders. In conclusion, I had a wonderful experience publishing in Brain and Neurological Disorders. The peer review process was thorough, the editorial office provided exceptional support, and the journal's quality is second to none. I would highly recommend this journal to any researcher working in the field of neurology and brain disorders.

Dear Agrippa Hilda, Journal of Neuroscience and Neurological Surgery, Editorial Coordinator, I trust this message finds you well. I want to extend my appreciation for considering my article for publication in your esteemed journal. I am pleased to provide a testimonial regarding the peer review process and the support received from your editorial office. The peer review process for my paper was carried out in a highly professional and thorough manner. The feedback and comments provided by the authors were constructive and very useful in improving the quality of the manuscript. This rigorous assessment process undoubtedly contributes to the high standards maintained by your journal.

International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews. I strongly recommend to consider submitting your work to this high-quality journal. The support and availability of the Editorial staff is outstanding and the review process was both efficient and rigorous.

Thank you very much for publishing my Research Article titled “Comparing Treatment Outcome Of Allergic Rhinitis Patients After Using Fluticasone Nasal Spray And Nasal Douching" in the Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology. As Medical Professionals we are immensely benefited from study of various informative Articles and Papers published in this high quality Journal. I look forward to enriching my knowledge by regular study of the Journal and contribute my future work in the field of ENT through the Journal for use by the medical fraternity. The support from the Editorial office was excellent and very prompt. I also welcome the comments received from the readers of my Research Article.

Dear Erica Kelsey, Editorial Coordinator of Cancer Research and Cellular Therapeutics Our team is very satisfied with the processing of our paper by your journal. That was fast, efficient, rigorous, but without unnecessary complications. We appreciated the very short time between the submission of the paper and its publication on line on your site.

I am very glad to say that the peer review process is very successful and fast and support from the Editorial Office. Therefore, I would like to continue our scientific relationship for a long time. And I especially thank you for your kindly attention towards my article. Have a good day!

"We recently published an article entitled “Influence of beta-Cyclodextrins upon the Degradation of Carbofuran Derivatives under Alkaline Conditions" in the Journal of “Pesticides and Biofertilizers” to show that the cyclodextrins protect the carbamates increasing their half-life time in the presence of basic conditions This will be very helpful to understand carbofuran behaviour in the analytical, agro-environmental and food areas. We greatly appreciated the interaction with the editor and the editorial team; we were particularly well accompanied during the course of the revision process, since all various steps towards publication were short and without delay".

I would like to express my gratitude towards you process of article review and submission. I found this to be very fair and expedient. Your follow up has been excellent. I have many publications in national and international journal and your process has been one of the best so far. Keep up the great work.

We are grateful for this opportunity to provide a glowing recommendation to the Journal of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy. We found that the editorial team were very supportive, helpful, kept us abreast of timelines and over all very professional in nature. The peer review process was rigorous, efficient and constructive that really enhanced our article submission. The experience with this journal remains one of our best ever and we look forward to providing future submissions in the near future.

I am very pleased to serve as EBM of the journal, I hope many years of my experience in stem cells can help the journal from one way or another. As we know, stem cells hold great potential for regenerative medicine, which are mostly used to promote the repair response of diseased, dysfunctional or injured tissue using stem cells or their derivatives. I think Stem Cell Research and Therapeutics International is a great platform to publish and share the understanding towards the biology and translational or clinical application of stem cells.

I would like to give my testimony in the support I have got by the peer review process and to support the editorial office where they were of asset to support young author like me to be encouraged to publish their work in your respected journal and globalize and share knowledge across the globe. I really give my great gratitude to your journal and the peer review including the editorial office.

I am delighted to publish our manuscript entitled "A Perspective on Cocaine Induced Stroke - Its Mechanisms and Management" in the Journal of Neuroscience and Neurological Surgery. The peer review process, support from the editorial office, and quality of the journal are excellent. The manuscripts published are of high quality and of excellent scientific value. I recommend this journal very much to colleagues.

Dr.Tania Muñoz, My experience as researcher and author of a review article in The Journal Clinical Cardiology and Interventions has been very enriching and stimulating. The editorial team is excellent, performs its work with absolute responsibility and delivery. They are proactive, dynamic and receptive to all proposals. Supporting at all times the vast universe of authors who choose them as an option for publication. The team of review specialists, members of the editorial board, are brilliant professionals, with remarkable performance in medical research and scientific methodology. Together they form a frontline team that consolidates the JCCI as a magnificent option for the publication and review of high-level medical articles and broad collective interest. I am honored to be able to share my review article and open to receive all your comments.

“The peer review process of JPMHC is quick and effective. Authors are benefited by good and professional reviewers with huge experience in the field of psychology and mental health. The support from the editorial office is very professional. People to contact to are friendly and happy to help and assist any query authors might have. Quality of the Journal is scientific and publishes ground-breaking research on mental health that is useful for other professionals in the field”.

Dear editorial department: On behalf of our team, I hereby certify the reliability and superiority of the International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews in the peer review process, editorial support, and journal quality. Firstly, the peer review process of the International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews is rigorous, fair, transparent, fast, and of high quality. The editorial department invites experts from relevant fields as anonymous reviewers to review all submitted manuscripts. These experts have rich academic backgrounds and experience, and can accurately evaluate the academic quality, originality, and suitability of manuscripts. The editorial department is committed to ensuring the rigor of the peer review process, while also making every effort to ensure a fast review cycle to meet the needs of authors and the academic community. Secondly, the editorial team of the International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews is composed of a group of senior scholars and professionals with rich experience and professional knowledge in related fields. The editorial department is committed to assisting authors in improving their manuscripts, ensuring their academic accuracy, clarity, and completeness. Editors actively collaborate with authors, providing useful suggestions and feedback to promote the improvement and development of the manuscript. We believe that the support of the editorial department is one of the key factors in ensuring the quality of the journal. Finally, the International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews is renowned for its high- quality articles and strict academic standards. The editorial department is committed to publishing innovative and academically valuable research results to promote the development and progress of related fields. The International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews is reasonably priced and ensures excellent service and quality ratio, allowing authors to obtain high-level academic publishing opportunities in an affordable manner. I hereby solemnly declare that the International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews has a high level of credibility and superiority in terms of peer review process, editorial support, reasonable fees, and journal quality. Sincerely, Rui Tao.

Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions I testity the covering of the peer review process, support from the editorial office, and quality of the journal.

Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions, we deeply appreciate the interest shown in our work and its publication. It has been a true pleasure to collaborate with you. The peer review process, as well as the support provided by the editorial office, have been exceptional, and the quality of the journal is very high, which was a determining factor in our decision to publish with you.
The peer reviewers process is quick and effective, the supports from editorial office is excellent, the quality of journal is high. I would like to collabroate with Internatioanl journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews journal clinically in the future time.

Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions, I would like to express my sincerest gratitude for the trust placed in our team for the publication in your journal. It has been a true pleasure to collaborate with you on this project. I am pleased to inform you that both the peer review process and the attention from the editorial coordination have been excellent. Your team has worked with dedication and professionalism to ensure that your publication meets the highest standards of quality. We are confident that this collaboration will result in mutual success, and we are eager to see the fruits of this shared effort.

Dear Dr. Jessica Magne, Editorial Coordinator 0f Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions, I hope this message finds you well. I want to express my utmost gratitude for your excellent work and for the dedication and speed in the publication process of my article titled "Navigating Innovation: Qualitative Insights on Using Technology for Health Education in Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients." I am very satisfied with the peer review process, the support from the editorial office, and the quality of the journal. I hope we can maintain our scientific relationship in the long term.
Dear Monica Gissare, - Editorial Coordinator of Nutrition and Food Processing. ¨My testimony with you is truly professional, with a positive response regarding the follow-up of the article and its review, you took into account my qualities and the importance of the topic¨.

Dear Dr. Jessica Magne, Editorial Coordinator 0f Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions, The review process for the article “The Handling of Anti-aggregants and Anticoagulants in the Oncologic Heart Patient Submitted to Surgery” was extremely rigorous and detailed. From the initial submission to the final acceptance, the editorial team at the “Journal of Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions” demonstrated a high level of professionalism and dedication. The reviewers provided constructive and detailed feedback, which was essential for improving the quality of our work. Communication was always clear and efficient, ensuring that all our questions were promptly addressed. The quality of the “Journal of Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions” is undeniable. It is a peer-reviewed, open-access publication dedicated exclusively to disseminating high-quality research in the field of clinical cardiology and cardiovascular interventions. The journal's impact factor is currently under evaluation, and it is indexed in reputable databases, which further reinforces its credibility and relevance in the scientific field. I highly recommend this journal to researchers looking for a reputable platform to publish their studies.
Dear Editorial Coordinator of the Journal of Nutrition and Food Processing! "I would like to thank the Journal of Nutrition and Food Processing for including and publishing my article. The peer review process was very quick, movement and precise. The Editorial Board has done an extremely conscientious job with much help, valuable comments and advices. I find the journal very valuable from a professional point of view, thank you very much for allowing me to be part of it and I would like to participate in the future!”

Dealing with The Journal of Neurology and Neurological Surgery was very smooth and comprehensive. The office staff took time to address my needs and the response from editors and the office was prompt and fair. I certainly hope to publish with this journal again.Their professionalism is apparent and more than satisfactory. Susan Weiner

My Testimonial Covering as fellowing: Lin-Show Chin. The peer reviewers process is quick and effective, the supports from editorial office is excellent, the quality of journal is high. I would like to collabroate with Internatioanl journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews.

My experience publishing in Psychology and Mental Health Care was exceptional. The peer review process was rigorous and constructive, with reviewers providing valuable insights that helped enhance the quality of our work. The editorial team was highly supportive and responsive, making the submission process smooth and efficient. The journal's commitment to high standards and academic rigor makes it a respected platform for quality research. I am grateful for the opportunity to publish in such a reputable journal.
My experience publishing in International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews was exceptional. I Come forth to Provide a Testimonial Covering the Peer Review Process and the editorial office for the Professional and Impartial Evaluation of the Manuscript.

I would like to offer my testimony in the support. I have received through the peer review process and support the editorial office where they are to support young authors like me, encourage them to publish their work in your esteemed journals, and globalize and share knowledge globally. I really appreciate your journal, peer review, and editorial office.
Dear Agrippa Hilda- Editorial Coordinator of Journal of Neuroscience and Neurological Surgery, "The peer review process was very quick and of high quality, which can also be seen in the articles in the journal. The collaboration with the editorial office was very good."

I would like to express my sincere gratitude for the support and efficiency provided by the editorial office throughout the publication process of my article, “Delayed Vulvar Metastases from Rectal Carcinoma: A Case Report.” I greatly appreciate the assistance and guidance I received from your team, which made the entire process smooth and efficient. The peer review process was thorough and constructive, contributing to the overall quality of the final article. I am very grateful for the high level of professionalism and commitment shown by the editorial staff, and I look forward to maintaining a long-term collaboration with the International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews.
To Dear Erin Aust, I would like to express my heartfelt appreciation for the opportunity to have my work published in this esteemed journal. The entire publication process was smooth and well-organized, and I am extremely satisfied with the final result. The Editorial Team demonstrated the utmost professionalism, providing prompt and insightful feedback throughout the review process. Their clear communication and constructive suggestions were invaluable in enhancing my manuscript, and their meticulous attention to detail and dedication to quality are truly commendable. Additionally, the support from the Editorial Office was exceptional. From the initial submission to the final publication, I was guided through every step of the process with great care and professionalism. The team's responsiveness and assistance made the entire experience both easy and stress-free. I am also deeply impressed by the quality and reputation of the journal. It is an honor to have my research featured in such a respected publication, and I am confident that it will make a meaningful contribution to the field.

"I am grateful for the opportunity of contributing to [International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews] and for the rigorous review process that enhances the quality of research published in your esteemed journal. I sincerely appreciate the time and effort of your team who have dedicatedly helped me in improvising changes and modifying my manuscript. The insightful comments and constructive feedback provided have been invaluable in refining and strengthening my work".

I thank the ‘Journal of Clinical Research and Reports’ for accepting this article for publication. This is a rigorously peer reviewed journal which is on all major global scientific data bases. I note the review process was prompt, thorough and professionally critical. It gave us an insight into a number of important scientific/statistical issues. The review prompted us to review the relevant literature again and look at the limitations of the study. The peer reviewers were open, clear in the instructions and the editorial team was very prompt in their communication. This journal certainly publishes quality research articles. I would recommend the journal for any future publications.

Dear Jessica Magne, with gratitude for the joint work. Fast process of receiving and processing the submitted scientific materials in “Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions”. High level of competence of the editors with clear and correct recommendations and ideas for enriching the article.

We found the peer review process quick and positive in its input. The support from the editorial officer has been very agile, always with the intention of improving the article and taking into account our subsequent corrections.

My article, titled 'No Way Out of the Smartphone Epidemic Without Considering the Insights of Brain Research,' has been republished in the International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews. The review process was seamless and professional, with the editors being both friendly and supportive. I am deeply grateful for their efforts.
To Dear Erin Aust – Editorial Coordinator of Journal of General Medicine and Clinical Practice! I declare that I am absolutely satisfied with your work carried out with great competence in following the manuscript during the various stages from its receipt, during the revision process to the final acceptance for publication. Thank Prof. Elvira Farina

Dear Jessica, and the super professional team of the ‘Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions’ I am sincerely grateful to the coordinated work of the journal team for the no problem with the submission of my manuscript: “Cardiometabolic Disorders in A Pregnant Woman with Severe Preeclampsia on the Background of Morbid Obesity (Case Report).” The review process by 5 experts was fast, and the comments were professional, which made it more specific and academic, and the process of publication and presentation of the article was excellent. I recommend that my colleagues publish articles in this journal, and I am interested in further scientific cooperation. Sincerely and best wishes, Dr. Oleg Golyanovskiy.

Dear Ashley Rosa, Editorial Coordinator of the journal - Psychology and Mental Health Care. " The process of obtaining publication of my article in the Psychology and Mental Health Journal was positive in all areas. The peer review process resulted in a number of valuable comments, the editorial process was collaborative and timely, and the quality of this journal has been quickly noticed, resulting in alternative journals contacting me to publish with them." Warm regards, Susan Anne Smith, PhD. Australian Breastfeeding Association.

Dear Jessica Magne, Editorial Coordinator, Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions, Auctores Publishing LLC. I appreciate the journal (JCCI) editorial office support, the entire team leads were always ready to help, not only on technical front but also on thorough process. Also, I should thank dear reviewers’ attention to detail and creative approach to teach me and bring new insights by their comments. Surely, more discussions and introduction of other hemodynamic devices would provide better prevention and management of shock states. Your efforts and dedication in presenting educational materials in this journal are commendable. Best wishes from, Farahnaz Fallahian.
Dear Maria Emerson, Editorial Coordinator, International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews, Auctores Publishing LLC. I am delighted to have published our manuscript, "Acute Colonic Pseudo-Obstruction (ACPO): A rare but serious complication following caesarean section." I want to thank the editorial team, especially Maria Emerson, for their prompt review of the manuscript, quick responses to queries, and overall support. Yours sincerely Dr. Victor Olagundoye.

Dear Ashley Rosa, Editorial Coordinator, International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews. Many thanks for publishing this manuscript after I lost confidence the editors were most helpful, more than other journals Best wishes from, Susan Anne Smith, PhD. Australian Breastfeeding Association.

Dear Agrippa Hilda, Editorial Coordinator, Journal of Neuroscience and Neurological Surgery. The entire process including article submission, review, revision, and publication was extremely easy. The journal editor was prompt and helpful, and the reviewers contributed to the quality of the paper. Thank you so much! Eric Nussbaum, MD
Dr Hala Al Shaikh This is to acknowledge that the peer review process for the article ’ A Novel Gnrh1 Gene Mutation in Four Omani Male Siblings, Presentation and Management ’ sent to the International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews was quick and smooth. The editorial office was prompt with easy communication.

Dear Erin Aust, Editorial Coordinator, Journal of General Medicine and Clinical Practice. We are pleased to share our experience with the “Journal of General Medicine and Clinical Practice”, following the successful publication of our article. The peer review process was thorough and constructive, helping to improve the clarity and quality of the manuscript. We are especially thankful to Ms. Erin Aust, the Editorial Coordinator, for her prompt communication and continuous support throughout the process. Her professionalism ensured a smooth and efficient publication experience. The journal upholds high editorial standards, and we highly recommend it to fellow researchers seeking a credible platform for their work. Best wishes By, Dr. Rakhi Mishra.

Dear Jessica Magne, Editorial Coordinator, Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions, Auctores Publishing LLC. The peer review process of the journal of Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions was excellent and fast, as was the support of the editorial office and the quality of the journal. Kind regards Walter F. Riesen Prof. Dr. Dr. h.c. Walter F. Riesen.

Dear Ashley Rosa, Editorial Coordinator, International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews, Auctores Publishing LLC. Thank you for publishing our article, Exploring Clozapine's Efficacy in Managing Aggression: A Multiple Single-Case Study in Forensic Psychiatry in the international journal of clinical case reports and reviews. We found the peer review process very professional and efficient. The comments were constructive, and the whole process was efficient. On behalf of the co-authors, I would like to thank you for publishing this article. With regards, Dr. Jelle R. Lettinga.

Dear Clarissa Eric, Editorial Coordinator, Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Studies, I would like to express my deep admiration for the exceptional professionalism demonstrated by your journal. I am thoroughly impressed by the speed of the editorial process, the substantive and insightful reviews, and the meticulous preparation of the manuscript for publication. Additionally, I greatly appreciate the courteous and immediate responses from your editorial office to all my inquiries. Best Regards, Dariusz Ziora

Dear Chrystine Mejia, Editorial Coordinator, Journal of Neurodegeneration and Neurorehabilitation, Auctores Publishing LLC, We would like to thank the editorial team for the smooth and high-quality communication leading up to the publication of our article in the Journal of Neurodegeneration and Neurorehabilitation. The reviewers have extensive knowledge in the field, and their relevant questions helped to add value to our publication. Kind regards, Dr. Ravi Shrivastava.

Dear Clarissa Eric, Editorial Coordinator, Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Studies, Auctores Publishing LLC, USA Office: +1-(302)-520-2644. I would like to express my sincere appreciation for the efficient and professional handling of my case report by the ‘Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Studies’. The peer review process was not only fast but also highly constructive—the reviewers’ comments were clear, relevant, and greatly helped me improve the quality and clarity of my manuscript. I also received excellent support from the editorial office throughout the process. Communication was smooth and timely, and I felt well guided at every stage, from submission to publication. The overall quality and rigor of the journal are truly commendable. I am pleased to have published my work with Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Studies, and I look forward to future opportunities for collaboration. Sincerely, Aline Tollet, UCLouvain.

Dear Ms. Mayra Duenas, Editorial Coordinator, International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews. “The International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews represented the “ideal house” to share with the research community a first experience with the use of the Simeox device for speech rehabilitation. High scientific reputation and attractive website communication were first determinants for the selection of this Journal, and the following submission process exceeded expectations: fast but highly professional peer review, great support by the editorial office, elegant graphic layout. Exactly what a dynamic research team - also composed by allied professionals - needs!" From, Chiara Beccaluva, PT - Italy.

Dear Maria Emerson, Editorial Coordinator, we have deeply appreciated the professionalism demonstrated by the International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews. The reviewers have extensive knowledge of our field and have been very efficient and fast in supporting the process. I am really looking forward to further collaboration. Thanks. Best regards, Dr. Claudio Ligresti
Dear Chrystine Mejia, Editorial Coordinator, Journal of Neurodegeneration and Neurorehabilitation. “The peer review process was efficient and constructive, and the editorial office provided excellent communication and support throughout. The journal ensures scientific rigor and high editorial standards, while also offering a smooth and timely publication process. We sincerely appreciate the work of the editorial team in facilitating the dissemination of innovative approaches such as the Bonori Method.” Best regards, Dr. Matteo Bonori.

I recommend without hesitation submitting relevant papers on medical decision making to the International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews. I am very grateful to the editorial staff. Maria Emerson was a pleasure to communicate with. The time from submission to publication was an extremely short 3 weeks. The editorial staff submitted the paper to three reviewers. Two of the reviewers commented positively on the value of publishing the paper. The editorial staff quickly recognized the third reviewer’s comments as an unjust attempt to reject the paper. I revised the paper as recommended by the first two reviewers.

Dear Maria Emerson, Editorial Coordinator, Journal of Clinical Research and Reports. Thank you for publishing our case report: "Clinical Case of Effective Fetal Stem Cells Treatment in a Patient with Autism Spectrum Disorder" within the "Journal of Clinical Research and Reports" being submitted by the team of EmCell doctors from Kyiv, Ukraine. We much appreciate a professional and transparent peer-review process from Auctores. All research Doctors are so grateful to your Editorial Office and Auctores Publishing support! I amiably wish our article publication maintained a top quality of your International Scientific Journal. My best wishes for a prosperity of the Journal of Clinical Research and Reports. Hope our scientific relationship and cooperation will remain long lasting. Thank you very much indeed. Kind regards, Dr. Andriy Sinelnyk Cell Therapy Center EmCell

Dear Editorial Team, Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions. It was truly a rewarding experience to work with the journal “Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions”. The peer review process was insightful and encouraging, helping us refine our work to a higher standard. The editorial office offered exceptional support with prompt and thoughtful communication. I highly value the journal’s role in promoting scientific advancement and am honored to be part of it. Best regards, Meng-Jou Lee, MD, Department of Anesthesiology, National Taiwan University Hospital.

Dear Editorial Team, Journal-Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions, “Publishing my article with Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions has been a highly positive experience. The peer-review process was rigorous yet supportive, offering valuable feedback that strengthened my work. The editorial team demonstrated exceptional professionalism, prompt communication, and a genuine commitment to maintaining the highest scientific standards. I am very pleased with the publication quality and proud to be associated with such a reputable journal.” Warm regards, Dr. Mahmoud Kamal Moustafa Ahmed

Dear Maria Emerson, Editorial Coordinator of ‘International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews’, I appreciate the opportunity to publish my article with your journal. The editorial office provided clear communication during the submission and review process, and I found the overall experience professional and constructive. Best regards, Elena Salvatore.

Dear Mayra Duenas, Editorial Coordinator of ‘International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews Herewith I confirm an optimal peer review process and a great support of the editorial office of the present journal
Dear Editorial Team, Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions. I am really grateful for the peers review; their feedback gave me the opportunity to reflect on the message and impact of my work and to ameliorate the article. The editors did a great job in addition by encouraging me to continue with the process of publishing.

Dear Cecilia Lilly, Editorial Coordinator, Endocrinology and Disorders, Thank you so much for your quick response regarding reviewing and all process till publishing our manuscript entitled: Prevalence of Pre-Diabetes and its Associated Risk Factors Among Nile College Students, Sudan. Best regards, Dr Mamoun Magzoub.

International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews is a high quality journal that has a clear and concise submission process. The peer review process was comprehensive and constructive. Support from the editorial office was excellent, since the administrative staff were responsive. The journal provides a fast and timely publication timeline.

Dear Maria Emerson, Editorial Coordinator of International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews, What distinguishes International Journal of Clinical Case Report and Review is not only the scientific rigor of its publications, but the intellectual climate in which research is evaluated. The submission process is refreshingly free of unnecessary formal barriers and bureaucratic rituals that often complicate academic publishing without adding real value. The peer-review system is demanding yet constructive, guided by genuine scientific dialogue rather than hierarchical or authoritarian attitudes. Reviewers act as collaborators in improving the manuscript, not as gatekeepers imposing arbitrary standards. This journal offers a rare balance: high methodological standards combined with a respectful, transparent, and supportive editorial approach. In an era where publishing can feel more burdensome than research itself, this platform restores the original purpose of peer review — to refine ideas, not to obstruct them Prof. Perlat Kapisyzi, FCCP PULMONOLOGIST AND THORACIC IMAGING.

Dear Grace Pierce, International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews I appreciate the opportunity to review for Auctore Journal, as the overall editorial process was smooth, transparent and professionally managed. This journal maintains high scientific standards and ensures timely communications with authors, which is truly commendable. I would like to express my special thanks to editor Grace Pierce for his constant guidance, promt responses, and supportive coordination throughout the review process. I am also greatful to Eleanor Bailey from the finance department for her clear communication and efficient handling of all administrative matters. Overall, my experience with Auctore Journal has been highly positive and rewarding. Best regards, Sabita sinha

Dear Mayra Duenas, Editorial Coordinator of the journal IJCCR, I write here a little on my experience as an author submitting to the International Journal of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews (IJCCR). This was my first submission to IJCCR and my manuscript was inherently an outsider’s effort. It attempted to broadly identify and then make some sense of life’s under-appreciated mysteries. I initially had responded to a request for possible submissions. I then contacted IJCCR with a tentative topic for a manuscript. They quickly got back with an approval for the submission, but with a particular requirement that it be medically relevant. I then put together a manuscript and submitted it. After the usual back-and-forth over forms and formality, the manuscript was sent off for reviews. Within 2 weeks I got back 4 reviews which were both helpful and also surprising. Surprising in that the topic was somewhat foreign to medical literature. My subsequent updates in response to the reviewer comments went smoothly and in short order I had a series of proofs to evaluate. All in all, the whole publication process seemed outstanding. It was both helpful in terms of the paper’s content and also in terms of its efficient and friendly communications. Thank you all very much. Sincerely, Ted Christopher, Rochester, NY.
